What are the different types of injection molding polishing?
- Chemical polishing
- Electropolishing
- Mechanical polishing
- Ultrasonic polishing
- Fluid polishing
When it comes to injection molding, the polishing types are all responsible for achieving a certain surface finish on the plastic product. The polishing can be done in a number of ways, such as through chemical, mechanical fluid, electrolytic, or even abrasive polishing. Once these polishes have been applied onto the mold component, they can result in glossy, matte, semi-glossy, satin, dull, or fine matte finish, depending on the requirements of the plastic product.
Many of these polishing techniques are employed by injection molding manufacturers to achieve a certain design on the product. These techniques have to be applied consistently throughout the mold component so that the resulting appearance is uniform and free from any defects. Continue reading to learn more.
Chemical Polishing
As the name suggests, chemical polishing is done onto a mold by way of a chemical solution. In this process, the chemical solution is poured onto a certain portion of the mold — usually in a convex appearance. This results in a mold that has a distinctively glossy or shiny appearance, which is ideal for any complicated workpiece.
One benefit of the chemical polishing method is its simplicity. The solution creates a gradual, but uniform chemical reaction with the mold that affects only the targeted area. Manufacturers can use this technique in different volumes of production, since it doesn’t require too many complex materials to perform. The mold-making process is also less time-consuming, allowing the production of multiple polished molds at any given time.
Electropolishing
Electropolishing, or electrolytic polishing is similar to chemical polishing, but with some slight differences. If in chemical polishing, there is still the presence of a cathodic reaction, this is not the case in electropolishing. Instead, this phase is removed, resulting in a much more consistent appearance on the prestressed steel or steel mold.
There are generally two phases involved in electropolishing which begins at the macroscopic and then at the low-light level. In the first phase, an electrolytic solution is poured onto the mold. This increases the smoothness of the surface.
However, the polishing is still not finished at this point. In order to get that bright and glossy finish, the mold has to undergo anodic polarization. This leaves a thin sheet or a film of metal over the surface, creating a glossy and reflective part on the mold.
Mechanical Polishing
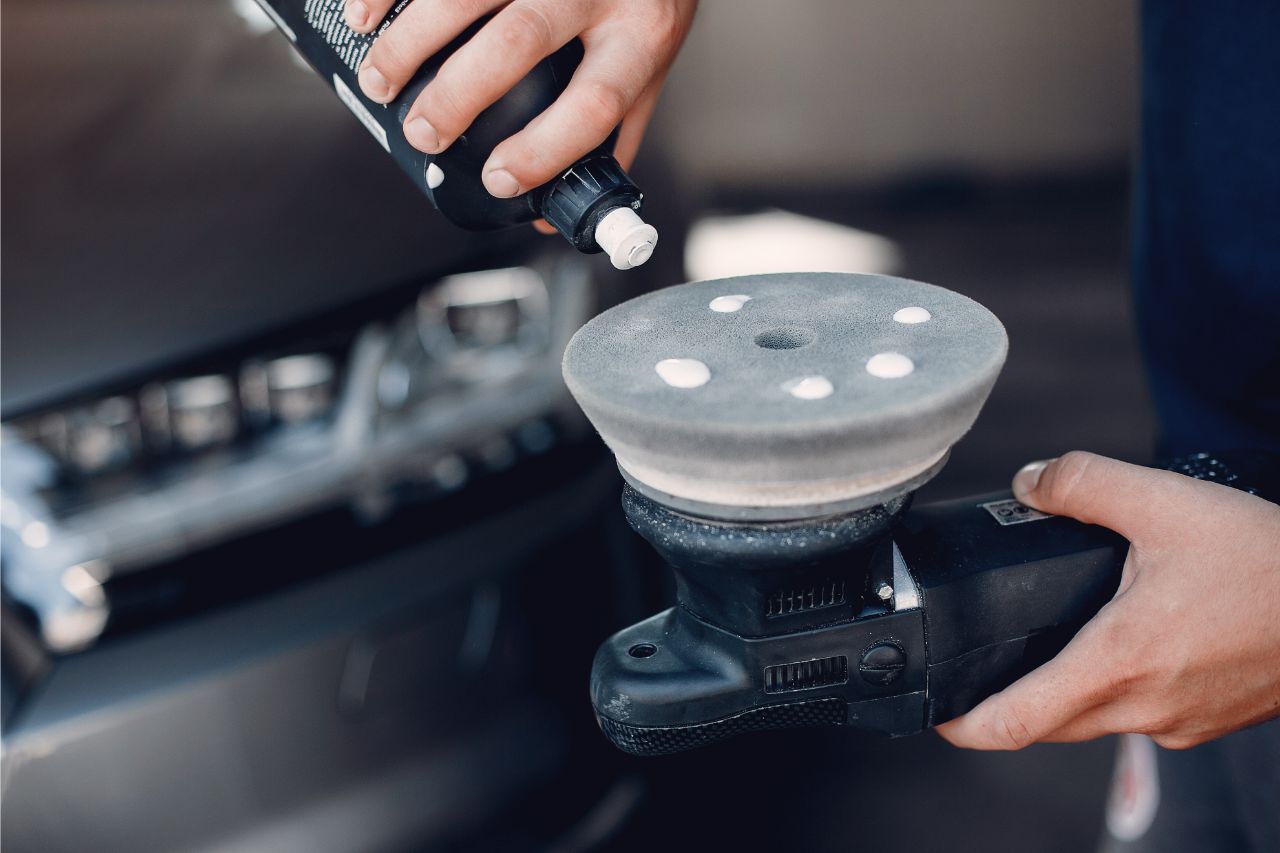

Mechanical polishing is arguably the least complicated and the most popular form of injection mold polishing. The polished effect is achieved by using a number of materials, depending on the preference of the manufacturer. Some common ones include spinning wheels, stones, sandpapers, and the like.
Since mechanical polishing is done by hand, this method may not necessarily be as productive compared to the previous two on the list. However, it is useful in the production of optic lenses for instruments like cameras, microscopes, telescopes, mirrors, magnifying glasses, and many more.
Oftentimes, mechanical polishing techniques are accompanied with abrasives and other fine materials. A machine is used to achieve a consistent rotating motion that applies the abrasives onto the mold and smoothens it.
Ultrasonic Polishing
Ultrasonic polishing is not necessarily a conventional technique, but it is useful when crafting molds that have higher tolerances, narrow areas, and small spaces. This is made possible by an ultrasonic machine that contains a handpiece to be used by the operator. Like mechanical polishing, the ultrasonic method also involves usage of a range of fine and coarse abrasives, like stones, ceramics, grit, brass laps, as well as diamond compounds.
Although ultrasonic polishing is not really widely-used for molds that have simple convex designs, they are ideal for high-precision molds. They can also significantly halve the lead time of mold manufacturing, allowing injection mold makers to produce higher output and increase manufacturing capacity.
Fluid Polishing
There are two main ingredients involved in fluid polishing — the polishing compound and the abrasive. The polishing compound is oftentimes made out of a polymeric substance composed of various proteins. This serves as the fluid, or the main medium by which the abrasives — silicon carbide powders — are deposited at a low pressure.
Although the method seems complicated, the method still results in a mold that achieves a desired polished result. One downside is that mold makers need to ensure that the fluid medium has been properly conveyed onto the mold in order to avoid any surface defects.
Key Takeaway
There you have it. You’ve learned about the five different injection molding polishing types that are used in creating a wide number of plastic injection molds.
These methods vary, depending on the technique as well as the medium used. Some processes may be more complicated than others and are used only for specific mold designs. Other methods, such as mechanical and chemical polishing are relatively simple, making them suitable for high-volume production.
In need of high-quality molds for your plastic parts? Richfields Plastics is capable of producing high-precision molds for OEM-grade or even custom-built parts. Click here to learn more about their products and services.