What are the differences between injection molding and blow molding?
- Process
- Types of Products
- Level of Waste Materials
- Volume of Production
Between the two processes of injection molding vs blow molding, there are several differences that you may encounter. Although they are both useful in the plastic manufacturing industry, the two methods have differences in the type of finished product, design complexity, or the cost of production.
Generally, blow molding is done to make finished plastic products that have distinct hollow shapes. On the other hand, injection molding is ideal for manufacturing applications that require complicated designs and multiple cavities.
Before choosing which technique to use, understanding their differences is the key to coming up with high-precision custom parts and other products that meet your requirements. Continue reading to learn more.
Process
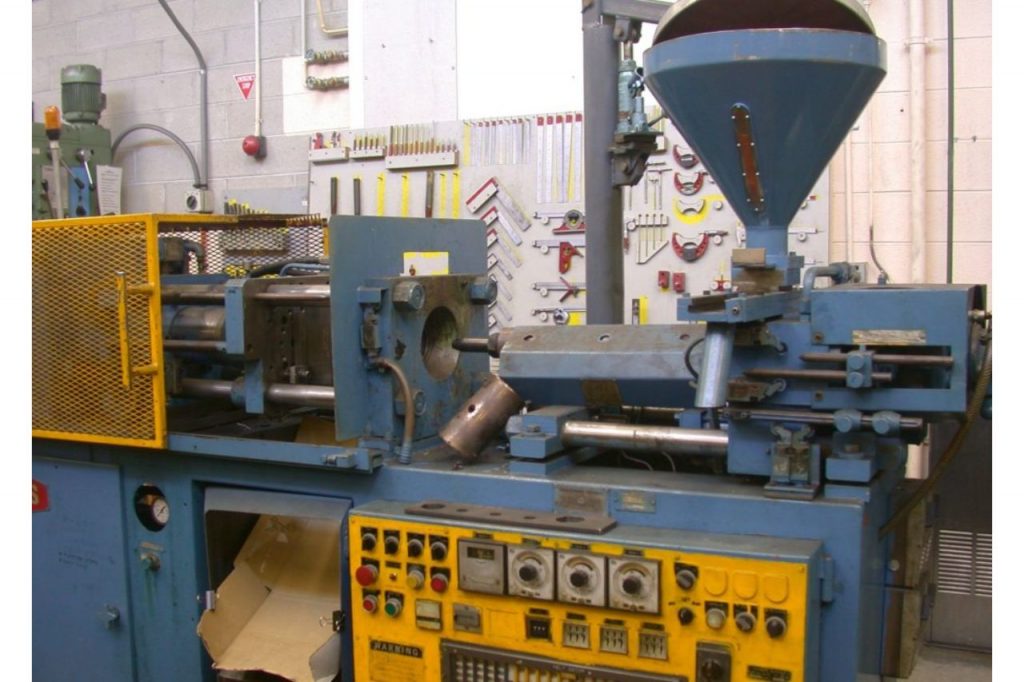
Similar to the injection molding process, blow molding starts off with resin or plastic pellets that have to be melted in order to shape it. Here’s a simple outline of the technique
- First, the plastic pellets are molten through a constant application of heat made possible by the multiple heat chambers present in the blow molding machine.
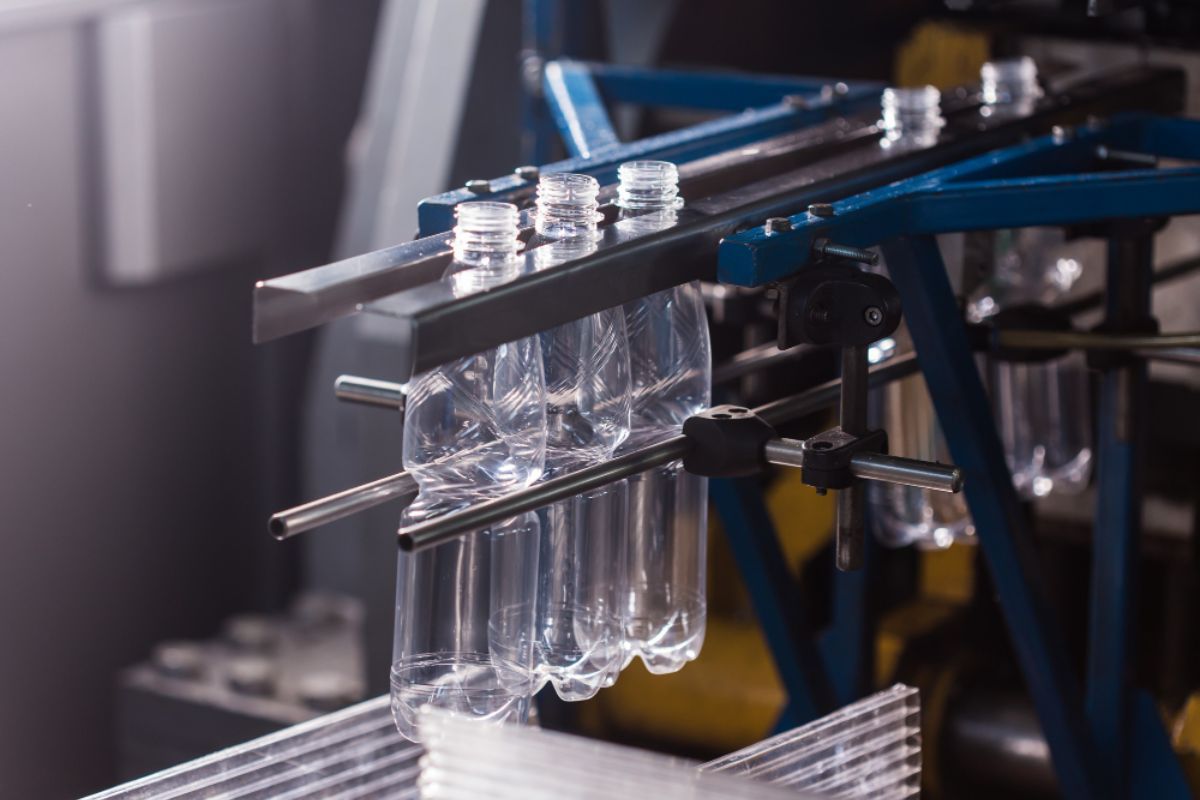
- The molten resins will then be transformed in order to have a tube-like shape called the parison.
- The parison is inserted into a two-part hollow mold that’s usually made from steel, or any kind of durable and hard-wearing alloy.
- Once secured in the mold, a high pressure air will be blown into the parison. This is done in order to expand the parison and fit it according to the shape of the hollow shape of the mold.
- After cooling, the finished product will now be ejected from the machine. It may now have to undergo post-processing techniques to remove any scrap or excess waste from the product.
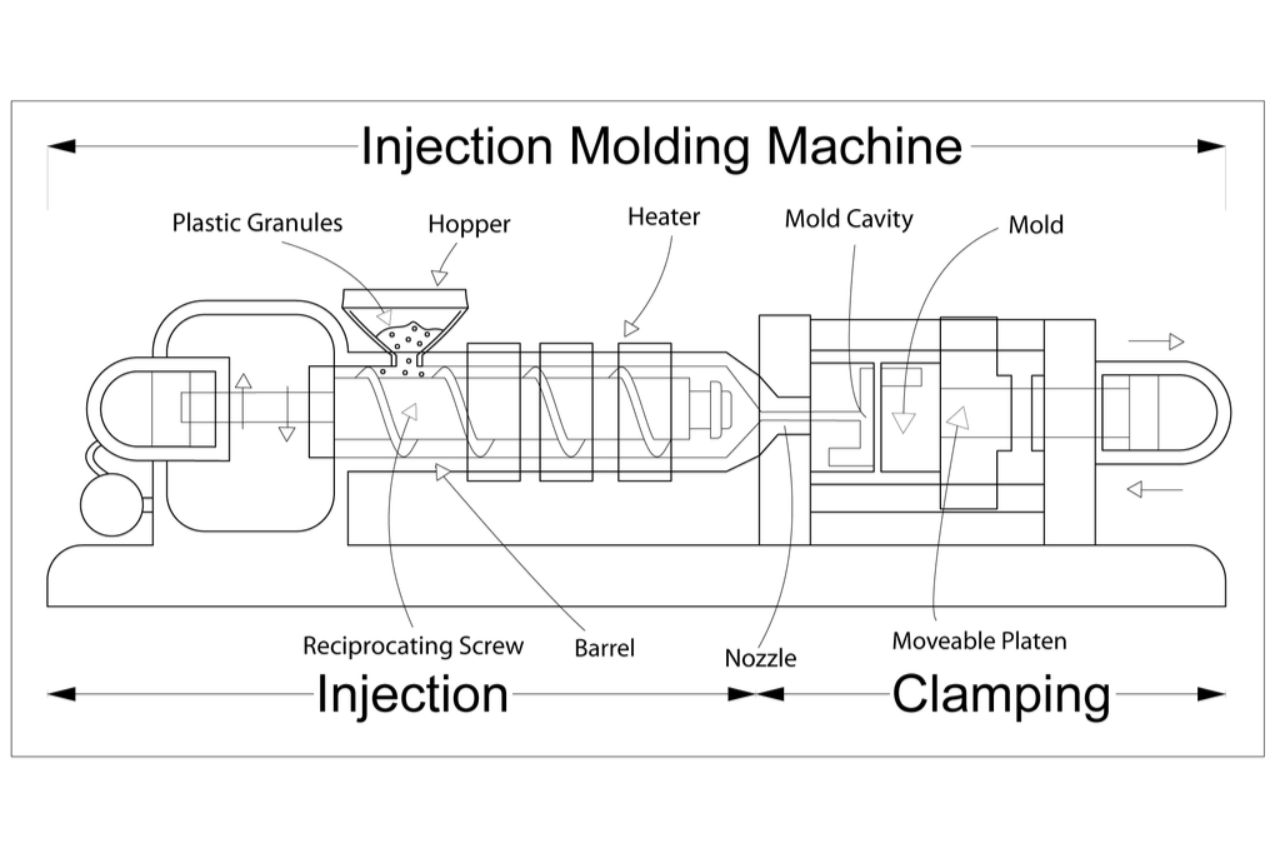
Injection molding on the other hand, starts off in a similar fashion. Here’s how:
- The plastic pellets are fed in the injection molding machine through the hoppers.
- In order to make sure that the molten resin remains in that consistency, various heat chambers are placed throughout the machine in order to heat it.
- Afterwhich, the molten plastic fluid is “injected” into the mold that can have numerous cavities, depending on the design.
- The molten plastic will adhere to the walls of the mold where it is then ejected after it has finished cooling.
Types of Products
Due to the limitations of the blow molding process, there are only a few handfuls of products/applications that can be done through this technique. This is due to the fact that the designs of the mold usually sport a hollow shape that can be used to manufacture containers of various kinds.
There are tons of consumer goods nowadays that are produced through blow molding. These can fall into the following: shampoo containers, facial wash bottles, small makeup tubes, and a range of other cosmetic containers.
With this in mind, the injection molding process is the better choice for producing plastic products that have complex shapes, such as bottle caps, car key fobs, phone casing, pipe fittings, shower hooks, automotive components, sports equipment parts, and so on.
Level of Waste Materials
Blow molding is a relatively simple process. While it may also require precision, its straightforward manufacturing phases allows it to produce a comparatively lower level of waste materials compared to injection molding.
As mentioned before, the blow molding process requires a molten parison that expands according to the design of the mold. Oftentimes, the final product can already be fit for distribution after it is ejected from the blow molding machine. Very rarely do manufacturers have to subject the product through post-processing.
Unlike blow molding, injection molding may still produce waste, especially in cold runner systems. The excess waste is usually due to the clamping mechanism that produces small plastic pieces attached to the product. Aside from this, there may also be molten resin left behind in the network of runners leading to the mold. All of these waste plastic materials still need to be cut as part of finishing touches on the plastic part.
Volume of Production
Injection molding can accommodate various mold types such as single-cavity, multi-cavity, or multi-family molds. In single-cavity molds, only one product can be manufactured in a single cycle time. Meanwhile, both multi-cavity and multi-family molds can be used for producing multiple plastic parts — whether similar or not — in one process.
In this aspect, blow molding has a disadvantage because it may be non-practical when it comes to high-volume production. Blow molding molds usually sport only one to two cavities, which result in far fewer finished products compared to injection molding.
Even if the cycle time for blow molding may be comparable — from as fast as 10 seconds to an average of 16 seconds — injection molding is still the better option for high-volume manufacturing of sophisticated plastic shapes and designs. Despite the high initial price of production, it’s still cost-effective in the long run.
Key Takeaway
In injection molding vs blow molding, you can spot a few differences regarding the processes involved, the level of product design, amount of waste materials generated, and the volume of production.
All of these factors should be considered before you choose the right method. Blow molding is fit for hollow shapes and designs, while injection molding is ideal for high-precision products.
In need of high-precision injection molding parts? Richfields Plastics can help you out! Click here to learn more about our services.