What are the different types of rubber molding processes?
- Rubber injection molding
- Compression molding
- Transfer molding
Molded rubber products have a myriad of uses. From vibration isolation to rubber-to-metal bonding, the applications are endless and can be found in various industries.
To make these products, manufacturers use rubber molding, the process of transforming uncured rubber via a metal mold cavity. In this process, chemical reactions take place and result in polymer chains in the material cross-link.
When using rubber molding, it’s important to choose the right methods to achieve your desired result. To help you understand the differences between methods, here’s a closer look at the three different types of rubber molding:
Rubber injection molding
Rubber injection molding is the ideal method for products that need to meet tight tolerances, and do so with high precision and accuracy.
In rubber injection molding, raw rubber is heated until liquid, which is then fed into a closed mold cavity under high pressure. This preheating process helps speed up the rubber’s curing time while allowing for higher curing temperatures.
This process can be done with a wide range of rubber materials, such as silicone, neoprene, EPDM, and nitrile. Injection molders opt for rubber injection molding to create a variety of molded rubber products.
Over the years, engineers have innovated this process and learned how to form rubber with increasing accuracy — resulting in three subcategories of rubber injection molding:
- Organic Rubber Injection
- Liquid Injection Molding or LSR Injection
- Thermoplastic Rubber Injection
These methods come with many advantages and few setbacks. Here’s a closer look at them:
Advantages of rubber injection molding
There are several benefits of using rubber injection molding, namely:
- Minimized material use and wastage.
- Faster cycle times.
- Faster production times.
- Higher dimensional tolerances.
Disadvantages of rubber injection molding
Likewise, there are a few things to note about using this method that might make it less suitable for your application, such as:
- Higher setup costs due to more expensive tooling and machinery.
- Some restrictions on the design of the tool — ultimately affecting the design of the finished part.
Compression molding
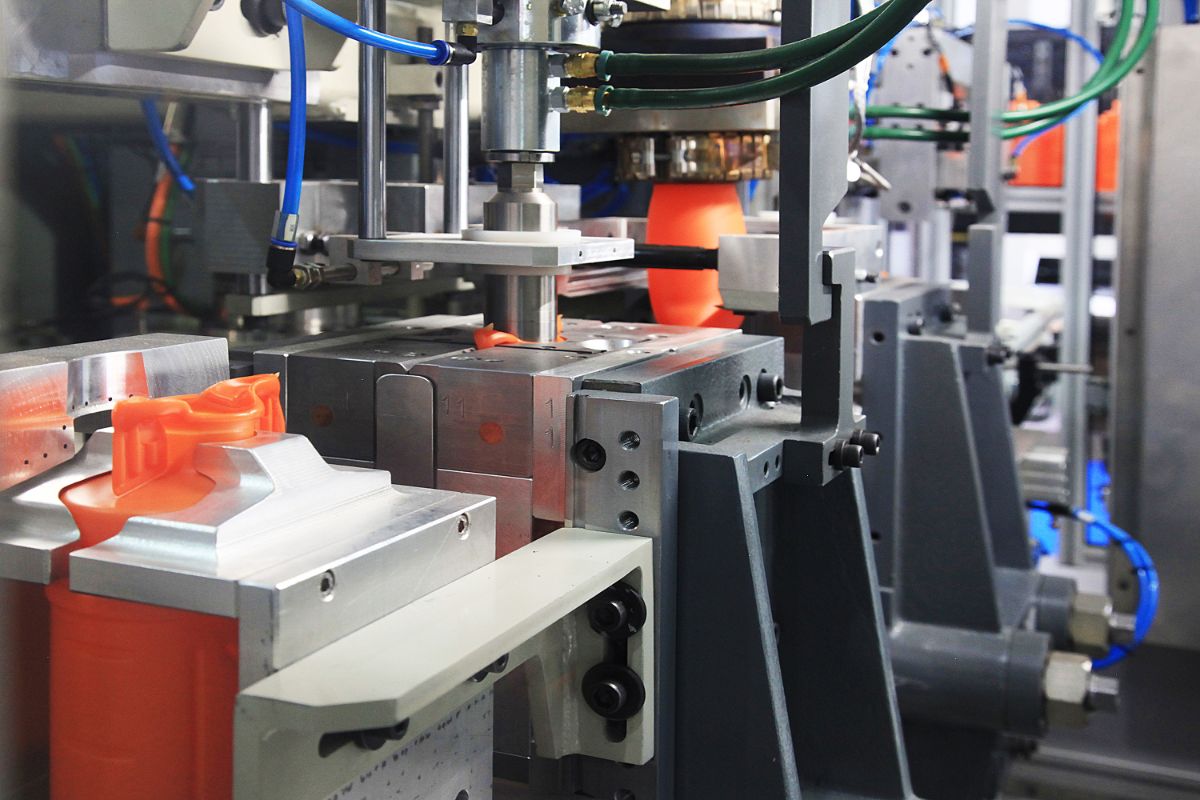

Compression molding is another type of rubber molding process and is considered the simplest type of them all.
In this process, a two-part, clamshell-style metal mold is used to shape rubber. Unvulcanized rubber is placed in this mold, which is then closed and heated. Once the rubber is flowing freely within the mold, and the appropriate temperature is reached, pressure is applied using a hydraulic press. This ensures the rubber is vulcanized and hardens to the right shape, which it will hold once it cools in the mold.
There are a few key advantages and disadvantages of compression molding:
Advantages of compression molding
The advantages of this type of rubber molding process include:
- Low levels of wastage.
- Simpler tooling costs, compared to rubber injection molding.
- Suitable for parts with large cross-sectional areas.
- Suitable for stiff, high durometer materials.
Disadvantages of compression molding
The setbacks of using this process are:
- Difficult to maintain consistency and high tolerances of finished parts.
- Slow cycle times and processing times.
Transfer molding
The way that transfer molding is done is somewhat like a combination of rubber injection molding and compression molding.
It uses a transfer system and a pot, which is where raw rubber compound is placed. From the pot, the rubber is forced by a heated plunger or piston through the transfer system.
The system is connected to the rubber mold through sprues and used to transfer raw rubber from the pot into multiple mold cavities after the press has been closed. This process allows the rubber to vulcanize, due to the heat and pressure used. When curing is completed, the mold is split open and the rubber parts are released.
This process is highly efficient, with short tool loading times — which allows it to be used for high production runs. Like with the other two methods, this comes with certain pros and cons:
Advantages of transfer molding
The pros of using transfer molding are:
- More accurate and consistent compared to compression molding.
- Shorter manufacturing times, due to the use of multiple mold cavities.
Disadvantages of transfer molding
The cons of using transfer molding are:
- More likely to result in material wastage.
- Transfer molding tools need more repair and maintenance than tools used in other processes.
- Designing intricate tooling for this process can be costly.
Key Takeaway
There are three types of rubber molding processes to choose from for your rubber product — each comes with its advantages and disadvantages. What sets each of them apart are your intended design and application, and how well you use these processes.
That said, honed skills and years of knowledge in this process are irreplaceable. That’s why working with Richfields — a full-service injection molding company in the USA with decades of experience in the field — is your best bet in creating a successful rubber molded product. Contact us today to receive professional consultancy and top services in design and manufacturing from our team!